Nexen Group, Inc. offers servomotor brakes with functional safety certification under its NexSafe trademark name. With ISO 13849-1 Functional Safety Certification, NexSafe brakes can be used for machine operations such as holding, emergency stopping or positioning. They are ideal for applications where safety is a priority.
Functional safety reduces the risk of injury posed by the use of machinery in the face of operator error or mechanical failure. Building functional safety requires the design and fabrication of protective features responding to human errors, hardware failures, operational or environmental stress. ISO 13849-1 is a safety of machinery standard that assists in the design and integration of safety related parts of control systems or machines. This standard includes a system of categorizing the risk a machine poses, and the safety functions to mitigate that risk.
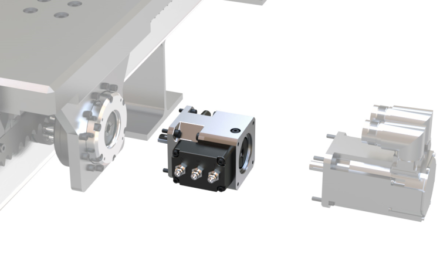
Servomotor brakes have been developed for braking on the shaft end of a servomotor or between a motor and gear reducer. The NexSafe servomotor brakes stop the load quickly and enhance safety with bidirectional braking capabilities. Typical applications include the production of automotive parts, cyclical operations, food production (IP67) and packaging, gantry routing, robotics, and semiconductors. The NexSafe servo brake shown in the picture can include up to three sensors to monitor the disengagement condition, engagement condition, and wear. This feedback helps the brake satisfies the requirements for functional safety certification and deliver IIoT connectivity.
Brake features to help achieve high levels of functional safety include multiple engagement springs that default to lock. The friction surfaces are equipped with a proprietary friction facing, tapered on both the inner and outer friction surfaces. Those surfaces apply the braking (locking) force via springs concurrently to both the rotating shaft and brake housing to hold the shaft from rotating, all with zero backlash. To ensure safe emergency stopping and holding, there are up to three operating-mode sensors for feedback. These are essentially inductive proximity sensors to sense three different brake conditions: First, disengagement: the proximity sensor in the brake activates when rated air pressure enters the brake’s the piston circuit to essentially pull the friction-facing pair apart, for a disengaged (free-running motor torque) axis condition. Second, engagement: the proximity sensor in the brake activates when the piston and facing friction-surface pair move into engagement and application of braking (stopping) torque. Third, wear: this proximity sensor in the brake activates when the brake is engaged but the friction facing is worn enough to necessitate replacement.
With spring-engaged, air-released functionality, NexSafe devices default to the locked position, making them ideal for holding a load in position or for emergency stopping situations. They can be used in any orientation. Nexen has manufactured thousands of rail brakes, servomotor brakes and rod locks for a wide range of applications. NexSafe builds on that experience, retaining form, fit, and functionality, while seeking enhanced safety. Industry 4.0 is a standard option all on NexSafe devices.
Contact for distribution in the UK: ICP Ltd.